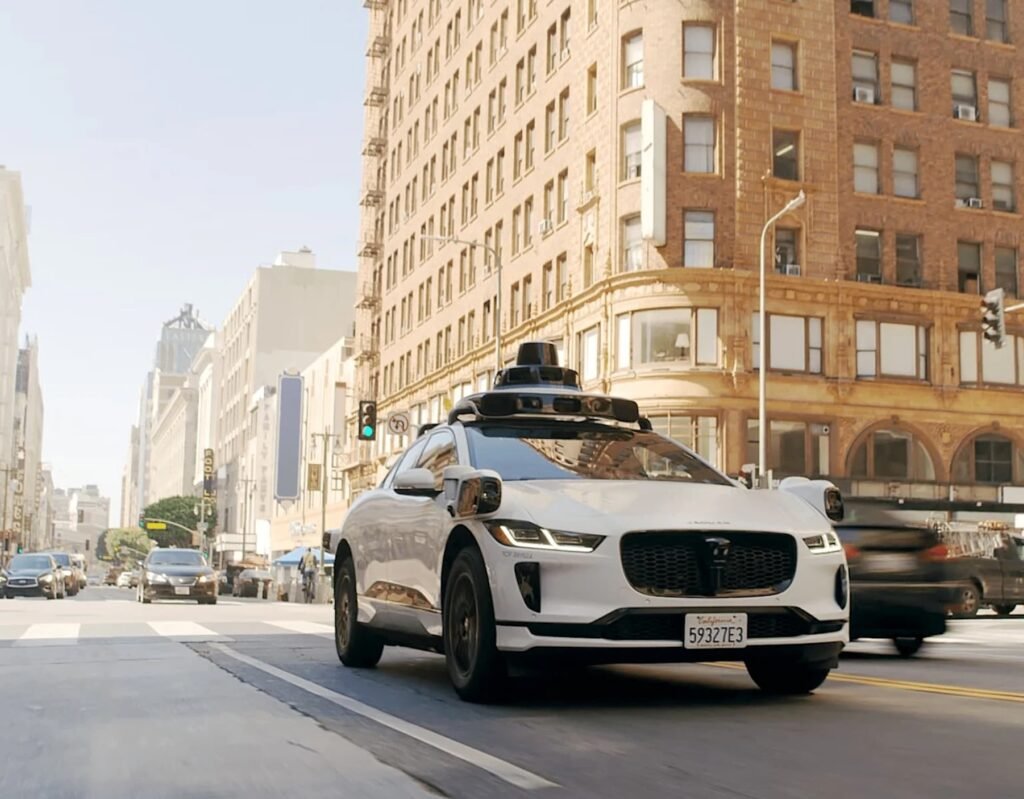
Imagine stepping into a car with no driver, no steering wheel, and no one shouting directions from the backseat. Instead, you’re welcomed by a quiet hum, a soft robotic voice confirming your destination, and the smooth motion of a vehicle completely in control of itself. No awkward small talk with a driver, no worries about distracted steering — just you, your thoughts, and the road ahead. This isn’t a sci-fi movie. This is Waymo.
Waymo is not just another tech company with bold claims — it’s the pioneer of autonomous driving. Born from Google’s famous self-driving car project, Waymo has evolved into the world’s most experienced autonomous driving platform. Whether it’s providing ride-hailing services in Phoenix or mapping the streets of San Francisco, Waymo cars are redefining how we move. These vehicles aren’t just programmed to drive — they’re designed to think, react, and learn like the safest driver you’ve ever met.
This blog post is your complete guide to Waymo. We’ll explore what it is, how it works, and why it’s reshaping the future of transportation. From the technology that powers these self-driving cars to their impact on safety, ethics, and the automotive industry, we’ll take a full ride through the world of Waymo — no driver required.
What Is Waymo?
Waymo is the self-driving technology company born from Google’s bold moonshot ambition. Originally launched in 2009 as part of Google X — the innovation lab behind Google’s wildest ideas — Waymo has since grown into a standalone subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., Google’s parent company. But more than a tech spin-off, Waymo represents a massive shift in how we think about mobility, autonomy, and trust in artificial intelligence.
At its core, Waymo’s mission is simple yet transformative: to make it safe and easy for people and things to move around. That mission goes far beyond replacing human drivers — it’s about reducing accidents, expanding access to transportation, and designing smarter cities. Over the years, Waymo has logged over 20 billion miles in simulation and tens of millions of real-world miles, making it the most experienced autonomous driving company on the planet.
Waymo’s services are built around two main pillars:
- Waymo One – This is Waymo’s fully autonomous ride-hailing service, currently available to the public in places like Phoenix, San Francisco, and soon, Los Angeles, Austin, and Atlanta. Users can summon a Waymo car through an app, just like Uber or Lyft — only without a human driver in sight.
- Waymo Via – Focused on autonomous delivery and freight, Waymo Via is designed to bring self-driving technology to trucks and cargo vans. It’s the quieter sibling of Waymo One but just as critical in shaping logistics and supply chains of the future.
So, if you’re wondering “Who owns Waymo?”, the answer is Alphabet — the same people behind Google Search, Gmail, and YouTube. That’s a lot of technological muscle behind the wheel.
How Waymo Works: The Technology Behind the Wheel
Have you ever tried to parallel park in a tight spot, with people watching, and your heart racing? Now imagine a car that can not only do that — but also navigate complex city streets, avoid reckless drivers, and adapt to unpredictable conditions — all without a single human touch. That’s the magic (and science) behind every Waymo self-driving car.

A 360-Degree Vision: Sensors Everywhere
To see the world clearly, Waymo cars are equipped with an impressive suite of sensors. We’re talking lidar (laser-based vision), radar (for detecting objects in rain or fog), and high-resolution cameras. Together, these tools allow the Waymo car to build a real-time, 360-degree view of its surroundings — pedestrians, cyclists, traffic signs, you name it.
Think of it as having multiple pairs of superhuman eyes that never blink, never get distracted, and never check their phone at a red light.
The Brain Behind the Wheel: AI and Machine Learning
Seeing is one thing. Making decisions? That’s where the real intelligence kicks in. Waymo uses advanced artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to understand and predict the behavior of other drivers, pedestrians, and even pets darting across the street. Every move the Waymo autonomous car makes is calculated with lightning speed based on thousands of variables.
This brain doesn’t just react — it learns. Thanks to simulation, it can practice millions of scenarios, from bizarre traffic events to rare emergency situations, in a risk-free digital environment before ever hitting the road.
The Digital Roadmap: HD Maps and Geofencing
Standard GPS won’t cut it here. Waymo cars rely on HD maps — ultra-detailed layouts of roads, lanes, curbs, traffic lights, and more. These maps are accurate down to the centimeter and constantly updated. In addition, geofencing defines the virtual boundaries within which Waymo cars operate. This ensures that the vehicles only drive in areas where the system has been trained and tested extensively.
So, when a Waymo taxi picks you up in San Francisco, it’s not just following directions — it’s navigating with a precision-guided memory of every inch of the route.
Waymo One: The Autonomous Ride-Hailing Service
Picture this: you’re in downtown Phoenix. You open an app, tap a button, and moments later, a sleek Waymo car glides silently to the curb. The doors unlock. There’s no driver. No small talk. Just you, your destination, and a quiet ride guided entirely by artificial intelligence. Welcome to Waymo One — the world’s first fully autonomous ride-hailing service.
Riding with Waymo: What It’s Like
If you’ve ever used Uber or Lyft, the concept is familiar. But Waymo One offers something radically different: no driver. Instead, you’re greeted by a voice from the car’s speaker system. The screen in front of you shows the route, nearby objects, and even explains why the car is slowing down or changing lanes.
There’s no awkward silence or questionable playlist — just smooth, calculated navigation. For many first-time riders, the experience feels like stepping into the future. And for returning riders? It quickly becomes the new normal.
Where You Can Ride: Waymo in the Wild
Waymo One isn’t just a tech demo — it’s live and operational in several U.S. cities, with full autonomy in some areas. Here’s where you can hop into a Waymo driverless car:
- Phoenix, Arizona: The flagship city for Waymo’s commercial rollout. Here, fully autonomous rides are available with no human backup driver — the Waymo taxi is 100% AI-driven.
- San Francisco, California: A more complex, urban environment where Waymo has been expanding rapidly. Hills, cyclists, and unpredictable traffic? Waymo handles it.
- Los Angeles, California and Austin, Texas: Currently in advanced testing and early rider programs.
- Atlanta, Georgia: Recently announced as a new city in Waymo’s expansion strategy.
Wondering where is Waymo available? Keep an eye on these hubs — and more cities are coming soon.
The Vehicles: High-Tech on Four Wheels
Waymo One uses specially equipped models designed for safety, comfort, and adaptability:
- Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid minivans: Roomy, smooth, and ideal for families.
- Jaguar I-PACE electric SUVs: Sleek, fast, and sustainable — with all the hardware for full autonomy seamlessly integrated.
These aren’t your average rides. Each Waymo self-driving car is packed with over a dozen sensors, onboard computers, and software systems working in real-time to ensure your journey is safe and smooth.
Is Waymo Cheaper than Uber?
This is a question many riders ask — and it depends. In some cases, Waymo fares are competitive with Uber and Lyft, especially during high-demand times when surge pricing hits traditional ride-shares. Plus, no tipping pressure or unexpected route changes. You’re paying for consistent, predictable, and safe service.
Over time, as Waymo scales and operating costs drop, it’s expected that Waymo taxi services could become even more affordable than human-driven alternatives.
Safety First: How Waymo Prioritizes Security
When people hear “self-driving car,” one of the first questions is always: Is it safe? It’s a fair concern — after all, you’re handing the wheel to an algorithm. But with Waymo, safety isn’t just a feature — it’s the foundation.
Millions of Miles, Thousands of Lessons
Waymo has driven over 20 million miles on public roads and simulated tens of billions of miles in virtual environments. That’s like driving every road in the U.S. — hundreds of times — without ever getting tired or distracted. Unlike humans, the Waymo Driver doesn’t text, drink, or get drowsy. It just… drives.
In Waymo Phoenix and Waymo San Francisco, where the cars are fully driverless, performance is constantly monitored and improved based on real-time data and edge cases. Every odd scenario — from rogue shopping carts to sudden rainstorms — becomes a learning opportunity for the AI.
Redundancy: Backups for the Backups
Waymo cars are built with layers of fail-safe systems. Think of it like flying a plane with multiple copilots and parachutes. Every critical component has a backup, and sometimes, a backup for the backup.
- Brakes? Redundant.
- Steering? Redundant.
- Computer systems? Doubly redundant.
So if anything goes wrong — a hardware glitch or a sensor hiccup — the car can still come to a controlled stop or reroute safely.
AI vs. Human Drivers
According to data from Waymo’s own safety reports and independent studies, Waymo cars are significantly less likely to be in a crash than human drivers. They react faster, follow traffic laws precisely, and never get aggressive behind the wheel.
And when something unexpected happens, like a pedestrian darting into the street, the Waymo self-driving car makes decisions in milliseconds — often faster than a human could even process what’s happening.
Government, Partnerships, and Oversight
Waymo doesn’t operate in a vacuum. It collaborates closely with:
- NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration)
- Local governments and DOTs
- Safety advocacy groups
These partnerships ensure that the technology isn’t just innovative — it’s held to strict standards for public trust and accountability.
Waymo’s Impact on the Automotive Industry
Self-driving technology isn’t just changing how we get from A to B — it’s reshaping the entire automotive industry from the ground up. And Waymo is right at the center of this transformation.
From Car Owners to Car Users
For over a century, owning a car was a rite of passage — a symbol of freedom and independence. But Waymo cars are redefining that idea. With services like Waymo One, people can now get around without ever owning a vehicle. No need for car payments, maintenance, insurance, or even a parking spot.
This shift toward Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) is causing traditional automakers to rethink their strategies. Companies like Jaguar and Chrysler have partnered with Waymo to adapt their vehicles for autonomous driving, showing that collaboration, not competition, is the way forward.
Reimagining the Car Itself
Because there’s no driver, Waymo can redesign what a car should be. Imagine a future where the front seats face each other like a lounge, or where the dashboard becomes an entertainment screen. No steering wheel. No pedals. Just space and comfort.
The concept of a Waymo driverless car forces automakers to ask: What will people do in a car when they’re not driving? That changes everything — from design and ergonomics to software and user experience.
Supply Chains and New Job Roles
Waymo’s technology is also influencing automotive supply chains. Traditional components, like manual gear systems or internal combustion engines, are becoming less relevant. Meanwhile, demand for high-performance sensors, AI chips, and connected systems is exploding.
This creates new job roles in robotics, machine learning, and cloud infrastructure — not to mention service teams that manage fleets of self-driving cars instead of selling individual units.
A Catalyst for Industry Innovation
Major players like Ford, GM, Tesla, and Mercedes are accelerating their autonomous programs, inspired — and pressured — by Waymo’s progress. While not all are aiming for full driverless capabilities, many now invest heavily in ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) to stay competitive.
In short, Waymo didn’t just enter the automotive space — it rewrote the rules. And the industry is following its lead.
Ethics, AI, and Responsibility: Who’s Behind the Wheel?
When there’s no human driver, who takes responsibility in an accident? Who makes life-or-death decisions in a split-second? These aren’t just technical questions — they’re deeply ethical ones. And Waymo is tackling them head-on.

Can You Teach Morality to a Machine?
A Waymo self-driving car doesn’t “think” like a human. It calculates probabilities, analyzes patterns, and makes decisions based on AI models trained on millions of scenarios. But what happens when it faces a true ethical dilemma — say, choosing between two bad outcomes?
Waymo’s approach is to avoid such scenarios altogether. Instead of asking the AI to play moral philosopher, the system is trained to minimize risk, avoid harm, and follow traffic laws at all times. It’s about safety-first logic, not emotion.
Still, the debate continues: Should machines be held to the same standards as people? Or higher ones?
Waymo Responsibility Without a Human Driver
With no one behind the wheel, the accountability shifts. If a Waymo autonomous car crashes, who’s at fault? The passenger? The programmer? Alphabet Inc.?
Waymo works closely with regulators to define new legal frameworks. Their vehicles are certified, insured, and audited in ways traditional cars never needed to be. And unlike a human driver, the Waymo Driver can be updated instantly — correcting issues across the entire fleet.
That makes accountability both scalable and transparent — but also brings new legal and social challenges.

Privacy, Data, and Trust
Waymo vehicles rely on real-time data: GPS, HD maps, Lidar, cameras — all capturing the world around them. That raises valid concerns about privacy.
What does Waymo do with this data? According to their policies, the focus is strictly on improving safety and performance. Data isn’t sold, and it’s anonymized whenever possible. Still, as with all AI systems, public trust depends on clear communication, oversight, and choice.
Designing Fairness Into the System
Waymo’s engineers also work to avoid bias in AI — ensuring the system performs just as safely in all neighborhoods, lighting conditions, and road types. This includes making the tech inclusive for people of all abilities, ages, and socioeconomic backgrounds.
In the end, ethics isn’t just a sidebar for Waymo — it’s built into the architecture of everything they create. Because when you take the human out of the driver’s seat, you have to double down on human values.
Market Opportunity and Business Model
Waymo isn’t just pioneering technology; it’s shaping a massive market that could redefine transportation as we know it. The autonomous vehicle market is projected to skyrocket — with estimates surpassing $800 billion by 2030. Waymo is positioned right at the forefront of this revolution.
Partnerships Fueling Growth
Waymo’s success hinges on strong collaborations. Alphabet has partnered with major automakers like Stellantis and Volvo to integrate its self-driving technology into a variety of vehicles. These partnerships not only accelerate innovation but also expand the potential reach of autonomous services.
In addition, Waymo’s business model includes licensing its Waymo Driver software to other companies, extending its influence beyond just the vehicles it owns and operates.
Monetizing Autonomy: Ride-Hailing and Beyond
The flagship service, Waymo One, generates revenue through autonomous ride-hailing. Customers pay per ride or through subscription models, enjoying a safer and often more cost-effective alternative to traditional taxis and rideshares.
Beyond passenger transport, Waymo Via focuses on freight and logistics. Autonomous trucks and delivery vans promise to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and address driver shortages in the shipping industry — a lucrative market in itself.
How Waymo Stands Apart
Compared to competitors like Tesla’s Autopilot or Cruise’s urban focus, Waymo offers:
- A fully autonomous system with no human backup driver in many areas.
- Extensive real-world miles and data powering its AI.
- A diverse fleet including minivans and electric SUVs.
- Broad geographic reach with growing presence in multiple U.S. cities.
This combination of technology, partnerships, and market strategy gives Waymo a distinct edge in the race toward widespread autonomous mobility.
Waymo Milestone: 100 Million Driverless Miles
In July 2025, Waymo hit a huge milestone: 100 million driverless miles driven — doubling the 50 million milestone reached at the end of 2024. This dramatic acceleration coincides with Waymo expanding its robotaxi service to cities including Los Angeles, Austin, Phoenix, Atlanta, and San Francisco, while planning to enter Washington, D.C., and New York City by 2026.
This growth isn’t just about numbers; it’s a clear sign of increasing public and industry trust in Waymo’s technology. As the company broadens its city coverage and increases ride frequency, it’s paving the way for broader adoption of autonomous mobility.
Social Impact: Making Mobility Inclusive
Waymo isn’t just transforming how we get around — it’s reshaping who gets to move freely and independently. Autonomous vehicles like Waymo’s self-driving car have the potential to break down barriers for millions who face transportation challenges every day.
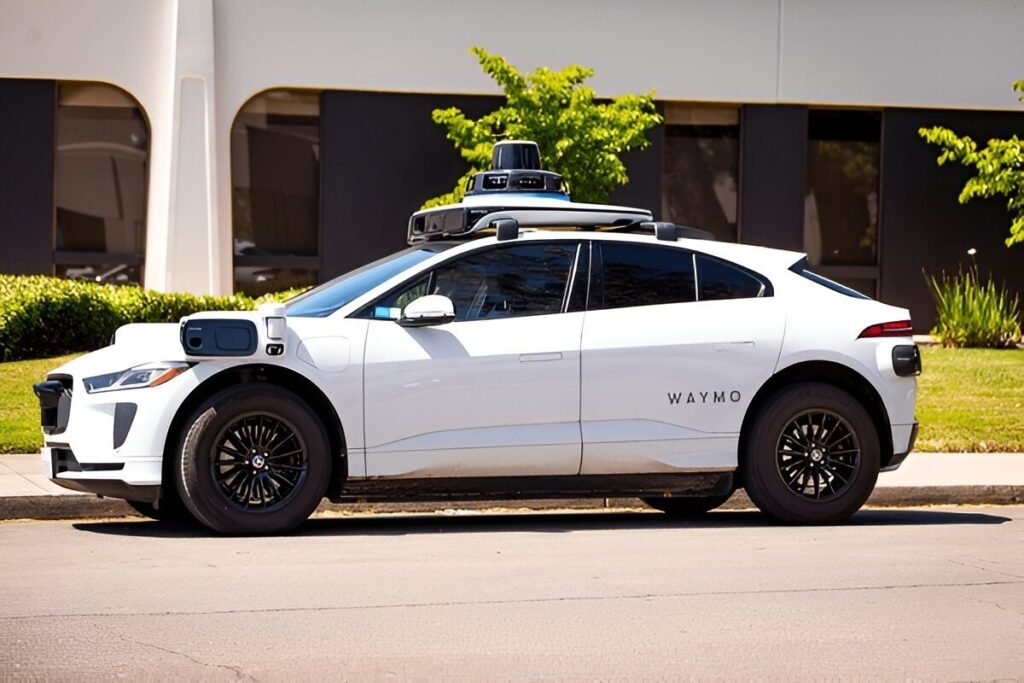

Empowering the Elderly and Disabled
For many seniors and people with disabilities, driving isn’t an option due to physical limitations or safety concerns. Waymo autonomous cars offer newfound freedom, allowing these individuals to reclaim independence without relying on family or costly private services.
Imagine an elderly person scheduling a Waymo taxi to get to a doctor’s appointment or a grocery store without needing assistance. It’s more than convenience — it’s dignity.
Bridging Transportation Deserts
In many suburban and rural areas, public transit is sparse or nonexistent. This creates “transportation deserts” where people struggle to access jobs, healthcare, and education.
Waymo’s expanding service areas, like Waymo Phoenix and soon Waymo Atlanta, aim to fill these gaps with reliable, on-demand rides. This helps connect underserved communities to opportunities, boosting economic inclusion.
Affordable, Accessible Mobility
Traditional taxis and rideshares can be expensive or inconvenient for some. With autonomous ride-hailing, costs are expected to come down as human labor is removed from the equation.
Waymo’s goal is to offer a service that is not only safer but also affordable and accessible, leveling the playing field for people across different income levels.
Waymo Challenges and Roadblocks
Even with all its promise, Waymo faces significant challenges on the road to full autonomy and widespread adoption.
Legal and Regulatory Hurdles
Autonomous vehicle laws vary widely between states and countries. Waymo must navigate a complex patchwork of regulations — from testing permissions to commercial ride-hailing approvals. This slows down expansion and adds uncertainty.
Technical Limitations
While Waymo’s AI is advanced, certain edge cases remain difficult: bad weather, complex construction zones, unpredictable pedestrian behavior. These situations require constant learning and updates.
Public Trust and Adoption
Despite millions of miles driven, some people remain skeptical or fearful of riding in a self-driving car. Building trust through transparency, education, and positive user experiences is critical.
Intense Competition
Waymo isn’t alone in the race. Tesla, Cruise, Zoox, Amazon, Baidu Apollo, and others are all developing autonomous systems — each with unique strengths and approaches.
Waymo must keep innovating to maintain its leadership position.
The Road Ahead: What’s Next for Waymo?
Waymo’s journey is far from over — it’s only just getting started. The company has bold plans to expand, innovate, and redefine transportation in the years ahead.
Expanding to New Cities and Regions
With successful deployments in Phoenix, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Austin, and Atlanta, Waymo is gearing up to bring its autonomous ride-hailing services to major hubs like Washington, D.C., and New York City by 2026. This expansion will expose more people to the convenience and safety of driverless cars.
Integrating with Smart Cities and IoT
Waymo is exploring deeper integration with smart city infrastructure — traffic signals, road sensors, and IoT devices — to enhance safety, reduce congestion, and optimize routes in real-time.
Advancing Toward Full Level 5 Autonomy
Currently, many Waymo vehicles operate without safety drivers, but the industry’s holy grail remains Level 5 autonomy — fully driverless cars that can handle any driving condition without human intervention. Waymo is steadily progressing toward this goal through continuous AI training and technology upgrades.
Waymo Vision of Zero Traffic Deaths
One of Waymo’s ultimate missions is to eliminate traffic fatalities. By removing human error — the cause of 94% of crashes — they envision a future where roads are safer for everyone.

Beyond Ride-Hailing: New Mobility Solutions
Waymo also plans to grow its autonomous trucking division, logistics services, and potentially even autonomous delivery robots, creating a comprehensive ecosystem of self-driving mobility.
Driving the Future: Why Waymo Matters
Waymo isn’t just building cars that drive themselves — it’s crafting the future of mobility. By pioneering autonomous driving technology, it’s opening doors to safer roads, greater accessibility, and a world where transportation is seamless and sustainable.
For everyday people, that means more freedom: the elderly regain independence, commuters save time, and cities breathe easier with fewer accidents and less congestion. Waymo’s journey highlights how technology, when designed thoughtfully and ethically, can transform our daily lives.
As Waymo expands its reach and overcomes challenges, it’s clear that driverless cars aren’t science fiction anymore. They’re a powerful reality rolling into our neighborhoods — and they’re here to stay.