Autonomous vehicles are no longer confined to science fiction—they’re rapidly becoming a transformative force on roads, seas, and even beneath the ocean’s surface. But what is an autonomous vehicle, really? And how close are we to fully autonomous vehicles reshaping our daily commutes and industries?
In recent years, the rise of self driving car autonomous vehicle technologies has sparked a surge of excitement and skepticism alike. As companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Cruise pour billions into AI in autonomous vehicle technology, the future seems closer than ever. Yet, challenges remain before we can rely entirely on these machines.
This article will explore the full spectrum of autonomous vehicles. From the levels of autonomous vehicles to market projections, limitations, and emerging opportunities, we’ll unpack what makes this technology one of the most astonishing innovations of our time.
What Is an Autonomous Vehicle?
The autonomous vehicles definition refers to a vehicle capable of sensing its environment and operating without human intervention. In simpler terms, what are autonomous vehicles? They are vehicles equipped with advanced sensors, AI systems, and machine learning algorithms that allow them to navigate roads, avoid obstacles, and make driving decisions independently.
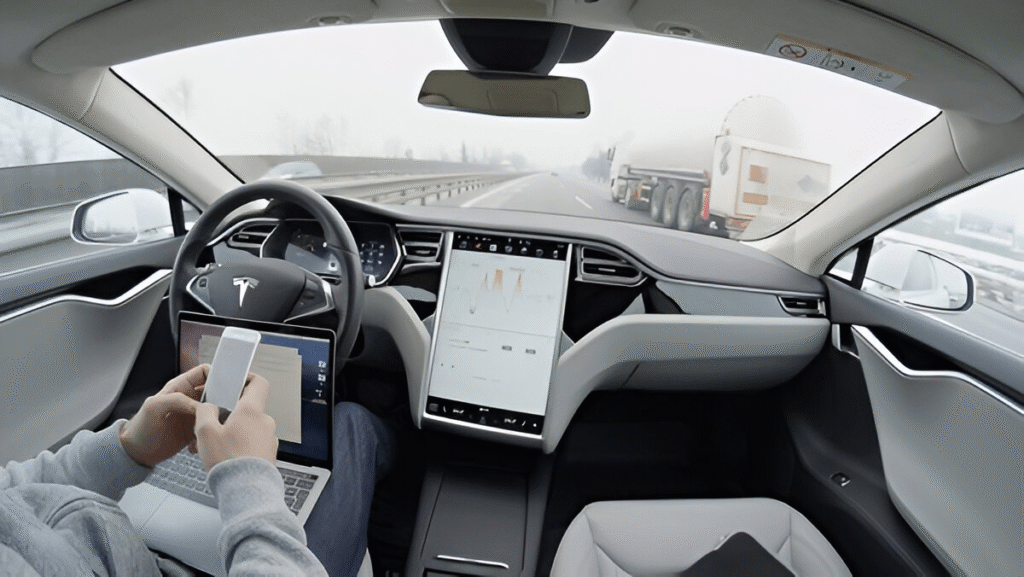

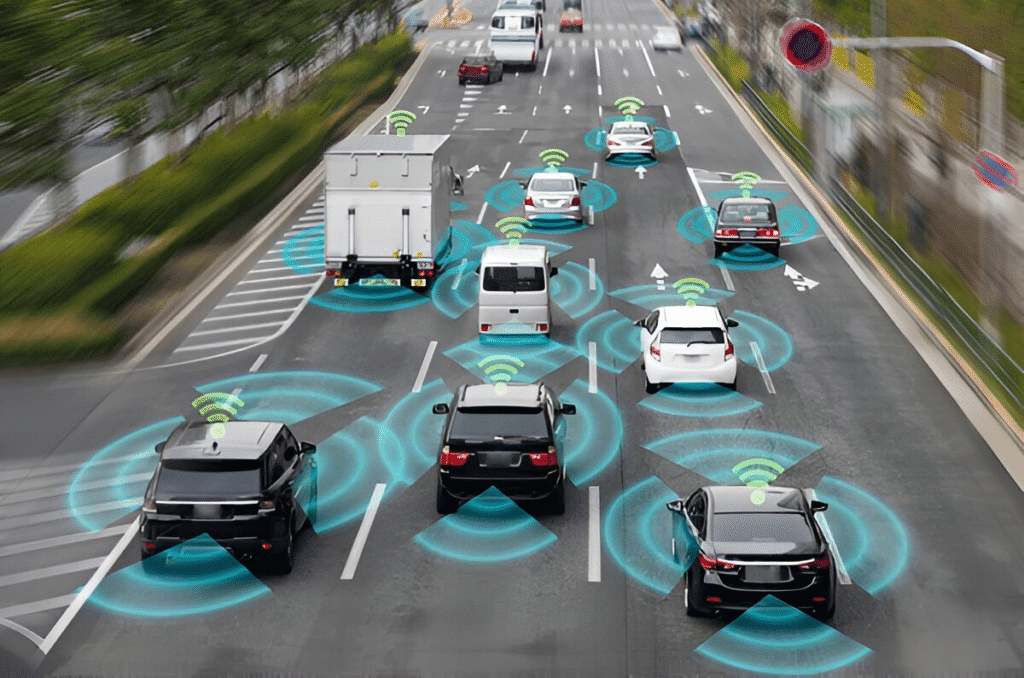
Self driving car autonomous vehicle systems rely on lidar, radar, cameras, and GPS. The goal is to create fully autonomous vehicles that can handle any driving scenario—rain, fog, complex traffic—without human assistance.
Beyond road transport, the concept expands into autonomous underwater vehicles and autonomous undersea vehicles. These machines navigate the depths of oceans autonomously, collecting valuable environmental data or aiding in exploration missions.
Levels of Vehicle Autonomy
Autonomous vehicles come with varying degrees of automation. The levels of autonomous vehicles, as defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), range from Level 0 to Level 5:
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Level 0 | No automation. The driver controls everything. |
| Level 1 | Driver assistance. Features like cruise control assist but don’t take over. |
| Level 2 | Partial automation. The car controls steering and acceleration under some conditions; the driver must stay attentive. |
| Level 3 | Conditional automation. The vehicle handles driving tasks, but human intervention is required if prompted. |
| Level 4 | High automation. The car manages most driving situations independently in specific environments. |
| Level 5 | Full automation. The vehicle is completely autonomous in all conditions, with no steering wheel or pedals required. |
Currently, companies like Tesla autonomous vehicles operate at Level 2, while Waymo autonomous vehicles and Cruise autonomous vehicle projects are piloting Level 4 technologies in controlled urban environments.
How People Can Use Autonomous Vehicles
Cruise autonomous vehicles and GM autonomous vehicle Cruise initiatives are paving the way for autonomous ride-hailing services. Riders in select cities can hail a self-driving car autonomous vehicle through an app, with no driver behind the wheel.
For businesses, autonomous vehicles trucks offer new logistics solutions. Self-driving trucks are already being tested for long-haul routes, promising reduced driver fatigue and optimized delivery schedules.
In maritime industries, autonomous underwater vehicles and autonomous undersea vehicles are revolutionizing data collection for oil exploration, marine biology, and defense.
Market Landscape and McKinsey Insights
According to McKinsey’s analysis, the autonomous vehicle market is expected to grow significantly by 2030, with an estimated 12% of new cars sold globally being fully autonomous vehicles. McKinsey highlights consumer demand for convenience and connected services as key drivers.
However, growth hinges on overcoming barriers such as public trust, regulatory approval, and cost reductions. Urban environments are likely to see the fastest adoption, driven by ride-sharing services like autonomous vehicles Uber and Cruise autonomous vehicles.
Fleet ownership models may dominate early adoption. Instead of individuals buying self driving car autonomous vehicle units, ride-hailing companies might operate fleets, reducing personal ownership in dense cities.
Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
The potential benefits of autonomous vehicles are wide-ranging:
- Safety: 94% of road accidents are due to human error. Autonomous vehicles promise to reduce crashes.
- Accessibility: People unable to drive, such as the elderly or disabled, gain mobility.
- Efficiency: Optimized routes and reduced congestion improve fuel consumption.
- Environmental Impact: Autonomous vehicles, particularly electric ones, could cut emissions by improving driving patterns.
In terms of fuel savings, estimates suggest autonomous vehicles could improve fuel economy by 10–30% through smoother acceleration and optimized traffic flows, depending on adoption levels and traffic conditions.
Existing Limitations and Barriers
Despite the promise, fully autonomous vehicles face hurdles:
- Technical Challenges: Poor weather, unpredictable human drivers, and complex road scenarios remain difficult for AI in autonomous vehicle technology.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Laws around autonomous vehicles vary widely, slowing deployment.
- Public Trust: Many consumers remain wary of handing control to a machine.
- High Costs: Lidar sensors and computing hardware are expensive, limiting affordability.
McKinsey warns that solving these challenges will require collaboration between automakers, tech firms, and regulators.
Autonomous Vehicles Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Fewer accidents | High development and production cost |
| Increased mobility | Job displacement in driving sectors |
| Improved traffic flow | Vulnerability to cyberattacks |
| Lower fuel consumption | Ethical dilemmas in accident scenarios |
Consumers must weigh the tradeoffs of autonomous vehicles pros and cons as the technology evolves.
The Role of AI in Autonomous Vehicle Technology
AI in autonomous vehicle technology is at the heart of autonomy. Machine learning systems process real-time data from cameras, radar, and lidar to make split-second driving decisions.
The AI must interpret signs, predict pedestrian behavior, and adapt to dynamic road conditions. Companies like Waymo and Cruise invest heavily in refining these AI models to reduce false positives and improve safety margins.
The Road Ahead
The journey toward autonomous vehicles is both astonishing and uncertain. What is an autonomous vehicle today may look very different in a decade, as advances push the boundaries of AI, connectivity, and mobility.
With players like Tesla autonomous vehicles, Cruise autonomous vehicles, and Waymo autonomous vehicles leading the charge, we’re witnessing a mobility revolution. Yet, until regulatory frameworks mature and public trust solidifies, widespread adoption will take time.
The astonishing world of autonomous vehicles promises more than driverless cars—it envisions a future where mobility is safer, greener, and more accessible. As the technology matures, consumers, businesses, and policymakers must navigate the road ahead thoughtfully.



Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.